It is easy to replace a conveyor belt by simply cutting off the old belt, removing it from the machine, lying it flat, and measuring its pre-tensioning length with a tape measure. If you do this, the conveyor will be out of commission until your new belts arrive. If you do this, you will experience significant downtime.
You have to order your replacement belt before the old belt fails, and you have to install the new belt immediately after removing the old belt. Know how to measure the conveyor belt and use the center-to-center distance formula when it is still in the conveyor belt system.
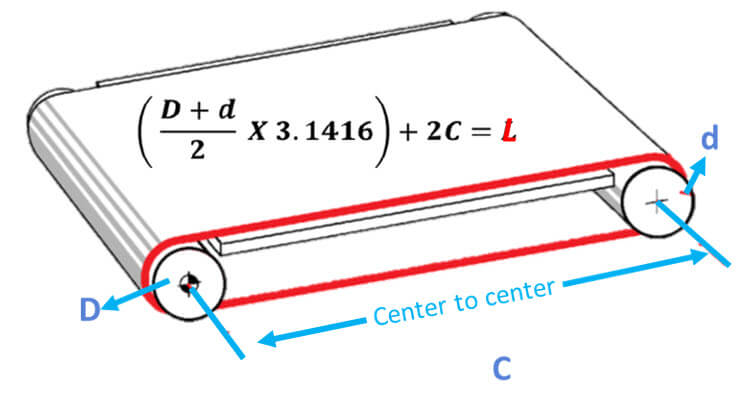
1. Center distance formula
This conveyor belt measurement formula is one of the most reliable methods to determine the correct length to replace the conveyor belt you need. The name of the formula refers to the distance between the belt drive center and the tail pulley. This is the formula:
Note: This formula only applies to 2 pulley systems
L = belt length (IN)
c = center-to-center distance (IN)
π = 3.1416
D = large pulley diameter (IN)
D=small pulley diameter (IN)
This math is not as difficult as it seems. This is the logic behind the center distance formula:
2c: The distance from center to center multiplied by 2 explains the belt length at the top and bottom of the pulley. Note: The pitch produced by different pulley diameters will be mentioned in the equation below.
(D+ D ÷ 2): This explains that the length of the belt is “wrapped” on the outside of the circumference of the pulley.
This calculation will give the stretched length of the belt. Be sure to pay attention to the takeover position on the system. If the take-up reaches the maximum, you can adjust them to the center position and re-measure the center-to-center distance. This will allow adjustments after the belt is running.
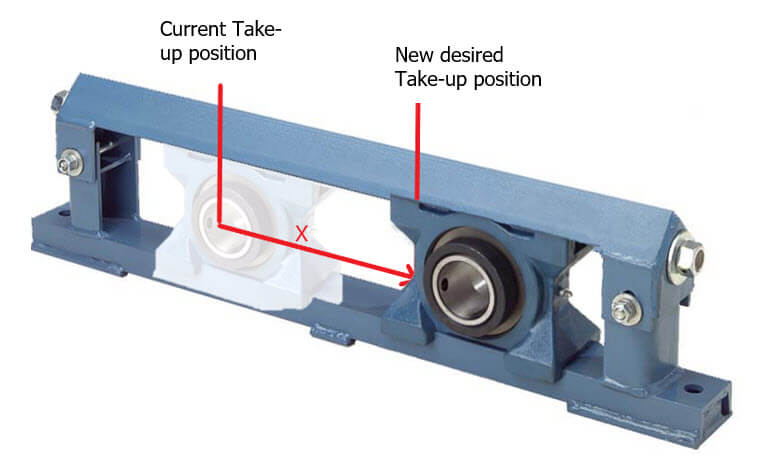
2. What is the effect of belt adjustment on belt length?
Many customers find it difficult to determine the belt length after adjusting the winding assembly. There is an easy way to calculate the change in belt length after coiling adjustment. But first, you need to solve this problem: Are you increasing or decreasing the length of the belt? If you are moving the reel to the end of the conveyor, then you will increase the existing belt length. If you are moving the conveyor in the center of the reel, then you will subtract the existing belt length (see the picture above).
X: adjust the required coiling volume
l1: Original belt length (before adjustment)
l2: The new length of the belt (after adjustment)
(2x) +/- l1 = l2
Note: You only need to double the winding adjustment distance (X) and add/subtract this number to the original belt length.
Example:
- The current belt length is 275″
- You are moving and fetching (close to the end of the conveyor) 5″
- You need to add 10 inches to the belt length (275 inches + 10 inches = 285 inches)
If you assemble a belt, the distance from center to center is unknown, or do you have more than 2 pulley systems?
In the case of more than 2 pulleys, the best way to obtain the belt length is to use the “start and stop” technique. Using this method, you will first need to mark a start mark on the top of the belt and mark it as “0”. Find the belt under the furthest distance, you can visit and make another mark on the top of the belt. You can then jog the system until the second mark is at the position of the first “0” mark, then lower the third mark by the same amount, and measure the distance between the marks. Continue this process until the final measurement ends with the mark “0”. Once you have the dimensions between all the marks, add them together and you will find the length of your conveyor belt.
Note: This process usually requires two people. Make sure that all hands, pens, and measuring equipment are off the belt before you jog the system.
3. Precision is the key
Incorrect measurement of center distance or pulley diameter, use of wrong tension or pre-stress, or mathematical errors will result in defective belt length calculations. The impact of ordering the wrong belt size is very serious:
- Extend downtime
- Additional cost
- Lower output
Therefore, it is crucial to double and triple check all measurements and calculations to ensure that the belts you receive have the appropriate specifications to keep your operations running smoothly and efficiently.